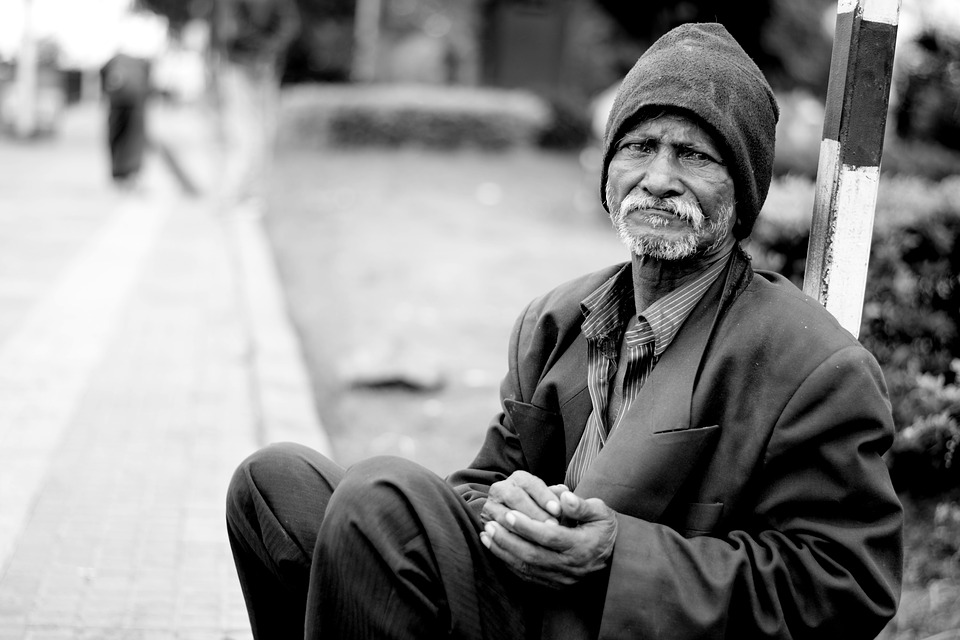
The city of Austin in the US state of Texas is developing a pilot project that uses the blockchain technology to collect and manage the identity information of the homeless population living in the city. The capital of Texas is developing this project as part of the Mayors Challenge 2018 organized by Bloomberg Philanthropies.
The goal is to win a subvention that could bring five million dollars that would be used for the development of the blockchain pilot project. Mayors Challenge 2018 is a national competition that rewards ingenious solutions for the problems the participating cities are facing.
Austin is competing in a group of 35 cities from the United States. Some of the competitors are: Doral, Florida; Detroit, Michigan and Los Angeles, California. According to the data published by Austin, more than 7,000 people living in the city are homeless and the lack of their identity management could cause problems when it comes to including them in the social care program. Austin’s project is the only participating project based on the blockchain technology.
Austin wrote in its participation form the following: “For the more than 7,000 people who experience homelessness in Austin, lack of ID can mean barriers to, or delays in, their access to housing, employment, and other services critical to dignity, support, and recovery.
The City of Austin will use blockchain technology to provide homeless residents with a unique identifier that allows them to access their personal records at any time, enabling access to critical services.”
According to Steve Adler, the mayor of Austin, the project is trying to find a solution for one of the biggest challenges the city is facing and that is to maintain all the information about a person with that person. Adler said: “at a high level, [the pilot] is trying to figure out how to solve one of the challenges we have in our community related to the homeless population, which is how to keep all the information of that individual with that individual. Austin is a creative, innovative city, and I’m excited we’re applying these core values to our approach to help those experiencing homelessness.”
Austin is a city with more than 947,000 inhabitants and the homeless population represents 0.73% of the total population. Blockchain has already been explored elsewhere for identity management, which means the Austin’s project could offer a real and practical solution to the problem. The blockchain technology could help verify the identity of a particular citizen, allowing the state to know what type of help he or she received and other important information. We are talking about detailed records that cannot be modified.
The goal of the Austin’s initiative is to consolidate the identity and the records of each homeless person and make this information accessible, secure and confidential, while providing a regulated access to the data stored in the blockchain network. The users can access their records, as well as social care workers. According to the mayor Adler, this can bring all kinds of confidentiality issues and that was the main reason why the city turned to the blockchain technology to bridge this problem.
Austin hopes to replace paper records because they are hard to manage and to introduce digital encrypted records that would be more reliable and provide better security. The blockchain technology would allow vital records to be built over time, which could allow various providers to access important information about their users.
It seems that identity is a very popular topic for investors in the blockchain technology.
Companies such as IBM are working on projects where the blockchain technology is used to keep records and manage the identity data. This way, the company cooperates with a non-profit organization called Sovrin to develop, operate and maintain a decentralized global network of digital identity based on the blockchain technology.
Likewise, Microsoft announced it was experimenting with a new project for identification based on the blockchain technology. This goal of the project is to store personal identification of each user in a blockchain network and to store personal information of the users outside the blockchain network, in an encrypted identity center that uses cryptographic keys to protect the information stored in it.